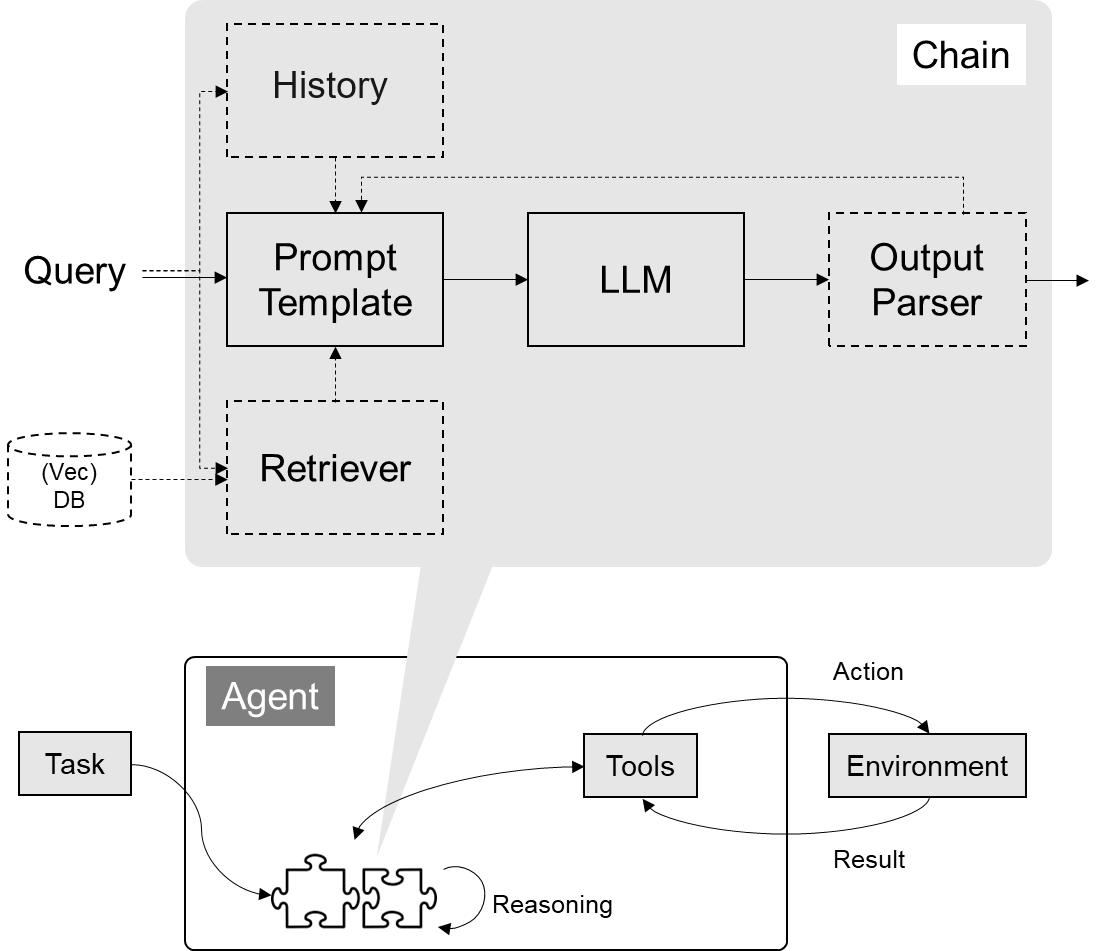
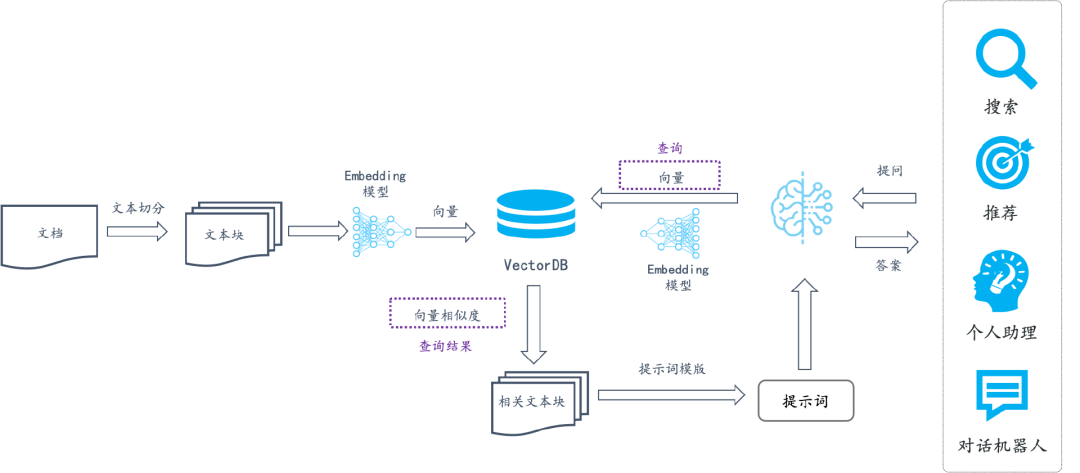
Graph RAG with Milvus
LLM的应用其响应准确性和相关性显的极其重要。检索增强生成(RAG)通过外部知识库增强模型能力,提供更丰富的上下文信息,减轻幻觉和知识不足等问题。然而,仅依赖简单的RAG范式存在局限性,特别是在处理复杂实体关系和多跳问题时,模型往往难以提供准确答案。
将知识图谱(KGs)引入RAG系统提供了新的解决方案。知识图谱以结构化方式呈现实体及其关系,提供更精确的检索信息,帮助RAG更好地处理复杂问答任务。KG-RAG仍处于早期阶段,目前对于如何有效从知识图谱中检索实体和关系,以及如何将向量相似度搜索与图结构集成,尚未达成共识。
在本笔记本中,我们介绍一种简单而强大的方法来显著提高这种场景下的性能。它是一种具有多路检索和重排序的简单RAG范式,但在逻辑上实现了图RAG,并在处理多跳问题方面达到了最先进的性能。
环境
! pip install --upgrade --quiet pymilvus numpy scipy langchain langchain-core langchain-openai tqdm
我们将使用来自OpenAI的模型。您需要准备[API密钥] OPENAI_API_KEY 作为环境变量。
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-***********"
以及引用必要的依赖
import numpy as np
from collections import defaultdict
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, HumanMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser, JsonOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from tqdm import tqdm
初始化 Milvus client, LLM, embedding model。
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
milvus_client = MilvusClient(
uri="http://172.16.53.94:19530",
token="root:Milvus"
)
#from openai import OpenAI
#openai_client = OpenAI(api_key="865***********************", base_url="https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3")
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="ep-20***************",
api_key="865***********************",
base_url="https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3",
temperature=0,
)
embedding_model = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="ep-20***************",
check_embedding_ctx_length=False,
api_key="865***********************",
base_url="https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3")
关于 MilvusClient 的参数:
- 将
uri设置为本地文件(例如./milvus.db)是最便捷的方法,它会自动利用 Milvus Lite 将所有数据存储在此文件中。- 如果您有大规模数据,可以在 Docker 或 Kubernetes 上搭建性能更优的 Milvus 服务器。在这种设置下,请使用服务器 URI(例如
http://localhost:19530)作为您的uri。- 如果您想使用 Milvus 的全托管云服务 Zilliz Cloud,请调整
uri和token参数,它们分别对应 Zilliz Cloud 中的 公共端点和 API 密钥。
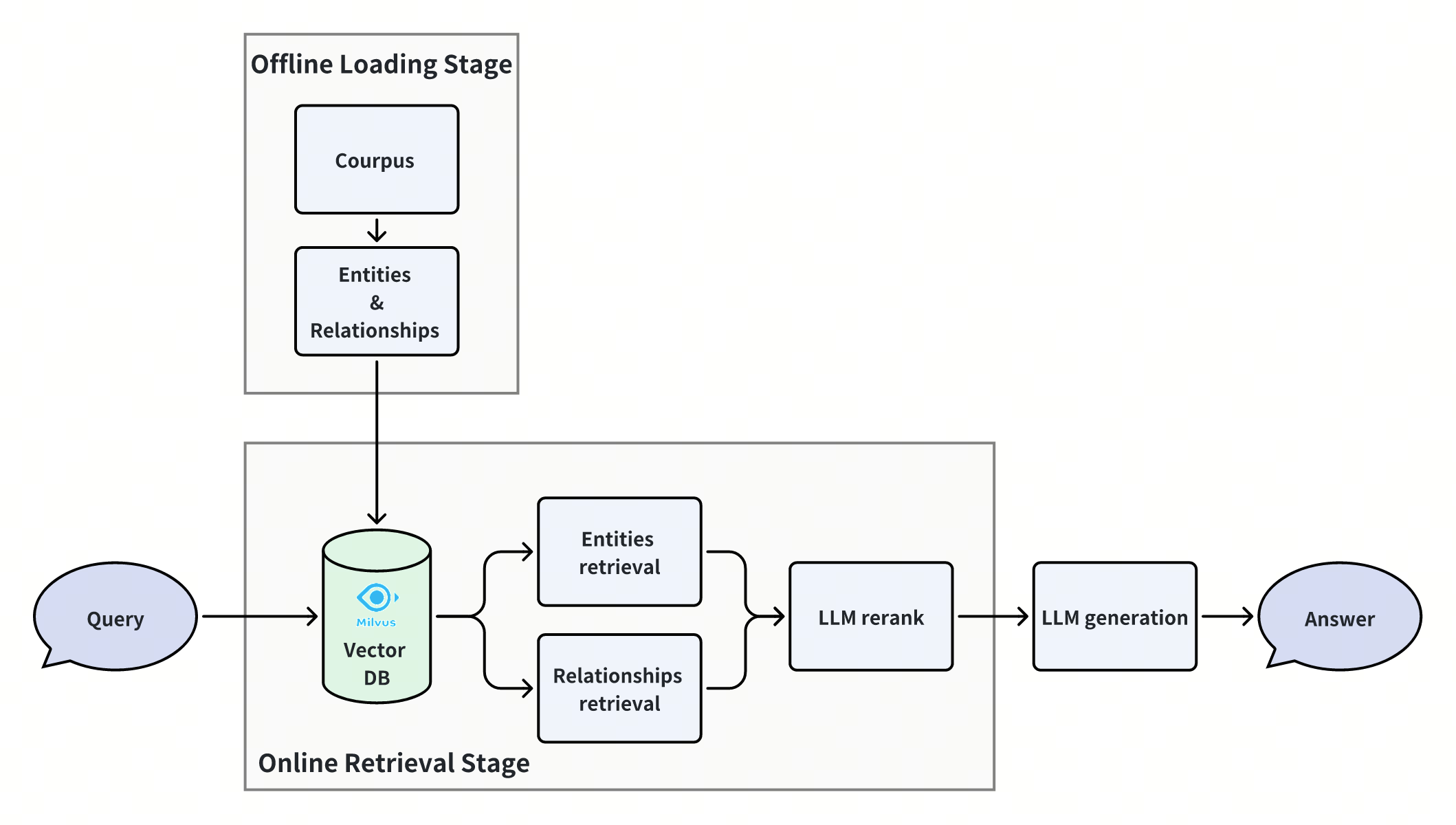
离线数据加载
数据准备
该小型数据集包含 4 个段落和一组对应的三元组,每个三元组包含主体(subject)、谓词(predicate)和客体(object)。在实际应用中,需要使用任何方法从自己的自定义语料中提取三元组。
nano_dataset = [
{
"passage": "Jakob Bernoulli (1654–1705): Jakob was one of the earliest members of the Bernoulli family to gain prominence in mathematics. He made significant contributions to calculus, particularly in the development of the theory of probability. He is known for the Bernoulli numbers and the Bernoulli theorem, a precursor to the law of large numbers. He was the older brother of Johann Bernoulli, another influential mathematician, and the two had a complex relationship that involved both collaboration and rivalry.",
"triplets": [
["Jakob Bernoulli", "made significant contributions to", "calculus"],
[
"Jakob Bernoulli",
"made significant contributions to",
"the theory of probability",
],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "is known for", "the Bernoulli numbers"],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "is known for", "the Bernoulli theorem"],
["The Bernoulli theorem", "is a precursor to", "the law of large numbers"],
["Jakob Bernoulli", "was the older brother of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
],
},
{
"passage": "Johann Bernoulli (1667–1748): Johann, Jakob’s younger brother, was also a major figure in the development of calculus. He worked on infinitesimal calculus and was instrumental in spreading the ideas of Leibniz across Europe. Johann also contributed to the calculus of variations and was known for his work on the brachistochrone problem, which is the curve of fastest descent between two points.",
"triplets": [
[
"Johann Bernoulli",
"was a major figure of",
"the development of calculus",
],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was", "Jakob's younger brother"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "worked on", "infinitesimal calculus"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was instrumental in spreading", "Leibniz's ideas"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "contributed to", "the calculus of variations"],
["Johann Bernoulli", "was known for", "the brachistochrone problem"],
],
},
{
"passage": "Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782): The son of Johann Bernoulli, Daniel made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.",
"triplets": [
["Daniel Bernoulli", "was the son of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "fluid dynamics"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "probability"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "made major contributions to", "statistics"],
["Daniel Bernoulli", "is most famous for", "Bernoulli’s principle"],
[
"Bernoulli’s principle",
"is fundamental to",
"the understanding of aerodynamics",
],
],
},
{
"passage": "Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.",
"triplets": [
[
"Leonhard Euler",
"had a significant relationship with",
"the Bernoulli family",
],
["leonhard Euler", "was born in", "Basel"],
["Leonhard Euler", "was a student of", "Johann Bernoulli"],
["Johann Bernoulli's influence", "was profound on", "Euler"],
],
},
]
按如下方式构建实体和关系:
- 实体是三元组中的主体(subject)或客体(object),因此我们直接从三元组中提取它们。
- 在这里,通过直接将主体、谓词和客体用空格连接起来来构建关系概念。
- 将实体 ID 映射到关系 ID,以及另一个字典,用于将关系 ID 映射到段落 ID
entityid_2_relationids = defaultdict(list)
relationid_2_passageids = defaultdict(list)
entities = []
relations = []
passages = []
for passage_id, dataset_info in enumerate(nano_dataset):
passage, triplets = dataset_info["passage"], dataset_info["triplets"]
passages.append(passage)
for triplet in triplets:
if triplet[0] not in entities:
entities.append(triplet[0])
if triplet[2] not in entities:
entities.append(triplet[2])
relation = " ".join(triplet)
if relation not in relations:
relations.append(relation)
entityid_2_relationids[entities.index(triplet[0])].append(
len(relations) - 1
)
entityid_2_relationids[entities.index(triplet[2])].append(
len(relations) - 1
)
relationid_2_passageids[relations.index(relation)].append(passage_id)
数据插入
创建用于实体、关系和段落的 Milvus 集合。在我们的方法中,实体集合和关系集合被用作图构建的主要集合,而段落集合则用于简单的 RAG 检索比较或辅助目的。
embedding_dim = len(embedding_model.embed_query("foo"))
def create_milvus_collection(collection_name: str):
if milvus_client.has_collection(collection_name=collection_name):
milvus_client.drop_collection(collection_name=collection_name)
milvus_client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
dimension=embedding_dim,
# Strong consistency waits for all loads to complete, adding latency with large datasets
# consistency_level="Strong",
)
entity_col_name = "entity_collection"
relation_col_name = "relation_collection"
passage_col_name = "passage_collection"
create_milvus_collection(entity_col_name)
create_milvus_collection(relation_col_name)
create_milvus_collection(passage_col_name)
将数据及其元数据信息插入到 Milvus 集合中,包括实体、关系和段落集合。元数据信息包括段落 ID 以及相邻的实体或关系 ID。
def milvus_insert(
collection_name: str,
text_list: list[str],
):
batch_size = 512
for row_id in tqdm(range(0, len(text_list), batch_size), desc="Inserting"):
batch_texts = text_list[row_id : row_id + batch_size]
batch_embeddings = embedding_model.embed_documents(batch_texts)
batch_ids = [row_id + j for j in range(len(batch_texts))]
batch_data = [
{
"id": id_,
"text": text,
"vector": vector,
}
for id_, text, vector in zip(batch_ids, batch_texts, batch_embeddings)
]
milvus_client.insert(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=batch_data,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=relation_col_name,
text_list=relations,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=entity_col_name,
text_list=entities,
)
milvus_insert(
collection_name=passage_col_name,
text_list=passages,
)
Inserting: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.01it/s]
Inserting: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.67it/s]
Inserting: 100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.71it/s]
在线查询
相似度检索
基于输入查询从 Milvus 中检索 topK 个相似的实体和关系。
在进行实体检索时,首先使用命名实体识别(NER)等特定方法从查询文本中提取查询实体。为简单起见,在此处准备了 NER 结果。如果想将查询更改为自定义问题,则必须更改相应的查询 NER 列表。在实际应用中,需使用任何其他模型或方法从查询中提取实体。
query = "What contribution did the son of Euler's teacher make?"
query_ner_list = ["Euler"]
# query_ner_list = ner(query) # In practice, replace it with your custom NER approach
query_ner_embeddings = [
embedding_model.embed_query(query_ner) for query_ner in query_ner_list
]
top_k = 3
entity_search_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=entity_col_name,
data=query_ner_embeddings,
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["id"],
)
query_embedding = embedding_model.embed_query(query)
relation_search_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=relation_col_name,
data=[query_embedding],
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["id"],
)[0]
print(relation_search_res)
[{'id': 20, 'distance': 0.8785505890846252, 'entity': {'id': 20}}, {'id': 18, 'distance': 0.874980092048645, 'entity': {'id': 18}}, {'id': 21, 'distance': 0.8671608567237854, 'entity': {'id': 21}}]
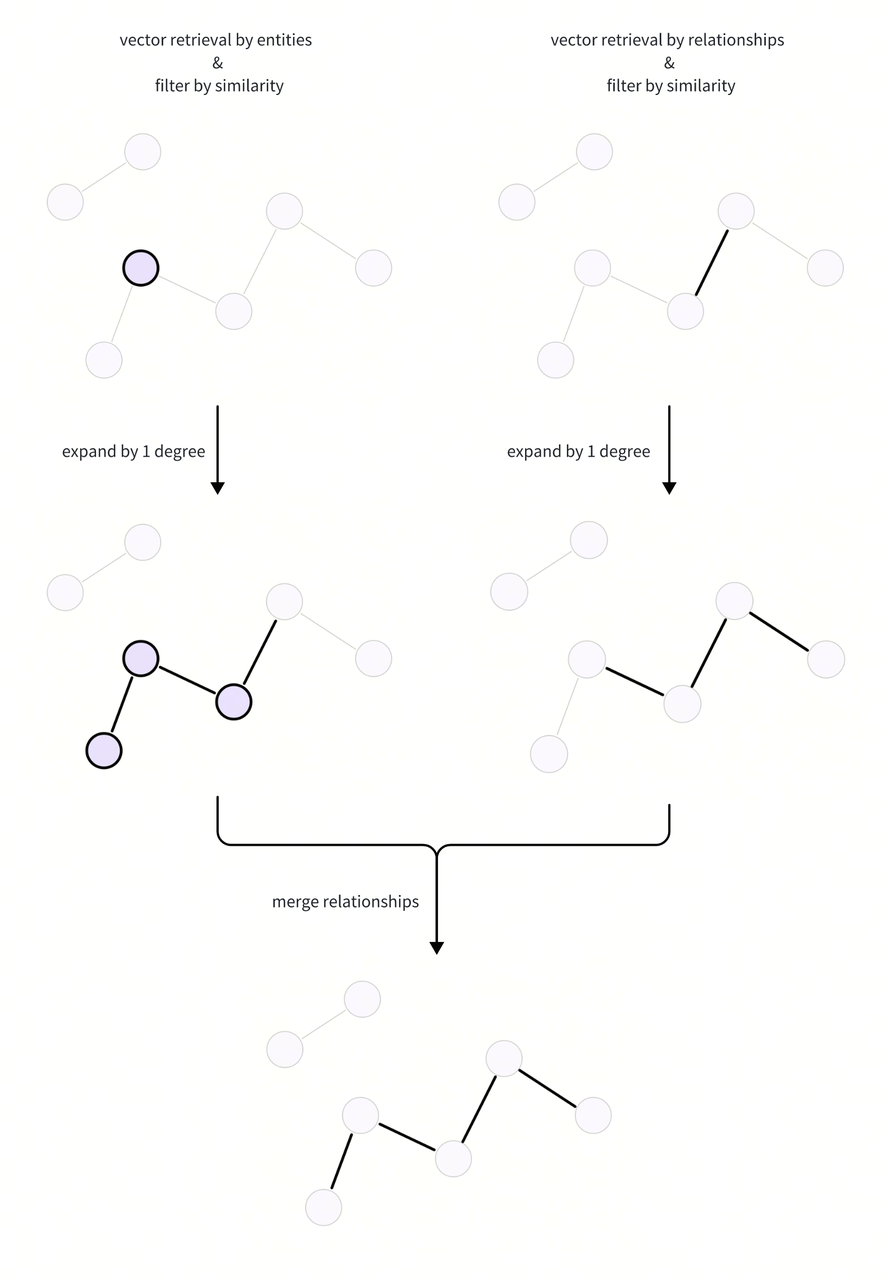
扩展子图
将检索到的实体和关系来扩展子图并获取候选关系,然后通过两种方式将它们合并。以下是子图扩展过程的流程图: 在构建邻接矩阵并使用矩阵乘法来计算几度内的邻接映射信息。通过这种方式,可以快速获取扩展度的信息。
# Construct the adjacency matrix of entities and relations where the value of the adjacency matrix is 1 if an entity is related to a relation, otherwise 0.
entity_relation_adj = np.zeros((len(entities), len(relations)))
for entity_id, entity in enumerate(entities):
entity_relation_adj[entity_id, entityid_2_relationids[entity_id]] = 1
# Convert the adjacency matrix to a sparse matrix for efficient computation.
entity_relation_adj = csr_matrix(entity_relation_adj)
# Use the entity-relation adjacency matrix to construct 1 degree entity-entity and relation-relation adjacency matrices.
entity_adj_1_degree = entity_relation_adj @ entity_relation_adj.T
relation_adj_1_degree = entity_relation_adj.T @ entity_relation_adj
# Specify the target degree of the subgraph to be expanded.
# 1 or 2 is enough for most cases.
target_degree = 1
# Compute the target degree adjacency matrices using matrix multiplication.
entity_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_1_degree
for _ in range(target_degree - 1):
entity_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_target_degree * entity_adj_1_degree
relation_adj_target_degree = relation_adj_1_degree
for _ in range(target_degree - 1):
relation_adj_target_degree = relation_adj_target_degree * relation_adj_1_degree
entity_relation_adj_target_degree = entity_adj_target_degree @ entity_relation_adj
通过从目标度扩展矩阵中取值,可以检索到的实体和关系中扩展相应的度,从而获取子图的所有关系。
expanded_relations_from_relation = set()
expanded_relations_from_entity = set()
# You can set the similarity threshold here to guarantee the quality of the retrieved ones.
# entity_sim_filter_thresh = ...
# relation_sim_filter_thresh = ...
filtered_hit_relation_ids = [
relation_res["entity"]["id"]
for relation_res in relation_search_res
# if relation_res['distance'] > relation_sim_filter_thresh
]
for hit_relation_id in filtered_hit_relation_ids:
expanded_relations_from_relation.update(
relation_adj_target_degree[hit_relation_id].nonzero()[1].tolist()
)
filtered_hit_entity_ids = [
one_entity_res["entity"]["id"]
for one_entity_search_res in entity_search_res
for one_entity_res in one_entity_search_res
# if one_entity_res['distance'] > entity_sim_filter_thresh
]
for filtered_hit_entity_id in filtered_hit_entity_ids:
expanded_relations_from_entity.update(
entity_relation_adj_target_degree[filtered_hit_entity_id].nonzero()[1].tolist()
)
# Merge the expanded relations from the relation and entity retrieval ways.
relation_candidate_ids = list(
expanded_relations_from_relation | expanded_relations_from_entity
)
relation_candidate_texts = [
relations[relation_id] for relation_id in relation_candidate_ids
]
LLM 重排序
利用 LLM 强大的自注意力机制进一步筛选和细化候选关系集。采用单样本提示(one-shot prompt),将查询和候选关系集整合到提示中,并指示 LLM 选择可能有助于回答查询的潜在关系。考虑到某些查询可能较为复杂,采用思维链(Chain-of-Thought)方法,允许 LLM 在其响应中阐述其思考过程。规定 LLM 的响应采用 JSON 格式,以便于解析。
query_prompt_one_shot_input = """I will provide you with a list of relationship descriptions. Your task is to select 3 relationships that may be useful to answer the given question. Please return a JSON object containing your thought process and a list of the selected relationships in order of their relevance.
Question:
When was the mother of the leader of the Third Crusade born?
Relationship descriptions:
[1] Eleanor was born in 1122.
[2] Eleanor married King Louis VII of France.
[3] Eleanor was the Duchess of Aquitaine.
[4] Eleanor participated in the Second Crusade.
[5] Eleanor had eight children.
[6] Eleanor was married to Henry II of England.
[7] Eleanor was the mother of Richard the Lionheart.
[8] Richard the Lionheart was the King of England.
[9] Henry II was the father of Richard the Lionheart.
[10] Henry II was the King of England.
[11] Richard the Lionheart led the Third Crusade.
"""
query_prompt_one_shot_output = """{"thought_process": "To answer the question about the birth of the mother of the leader of the Third Crusade, I first need to identify who led the Third Crusade and then determine who his mother was. After identifying his mother, I can look for the relationship that mentions her birth.", "useful_relationships": ["[11] Richard the Lionheart led the Third Crusade", "[7] Eleanor was the mother of Richard the Lionheart", "[1] Eleanor was born in 1122"]}"""
query_prompt_template = """Question:
{question}
Relationship descriptions:
{relation_des_str}
"""
def rerank_relations(
query: str, relation_candidate_texts: list[str], relation_candidate_ids: list[str]
) -> list[int]:
relation_des_str = "\n".join(
map(
lambda item: f"[{item[0]}] {item[1]}",
zip(relation_candidate_ids, relation_candidate_texts),
)
).strip()
rerank_prompts = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
HumanMessage(query_prompt_one_shot_input),
AIMessage(query_prompt_one_shot_output),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(query_prompt_template),
]
)
rerank_chain = (
rerank_prompts
| llm.bind(response_format={"type": "json_object"})
| JsonOutputParser()
)
rerank_res = rerank_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "relation_des_str": relation_des_str}
)
rerank_relation_ids = []
rerank_relation_lines = rerank_res["useful_relationships"]
id_2_lines = {}
for line in rerank_relation_lines:
id_ = int(line[line.find("[") + 1 : line.find("]")])
id_2_lines[id_] = line.strip()
rerank_relation_ids.append(id_)
return rerank_relation_ids
rerank_relation_ids = rerank_relations(
query,
relation_candidate_texts=relation_candidate_texts,
relation_candidate_ids=relation_candidate_ids,
)
最终结果
final_top_k = 2
final_passages = []
final_passage_ids = []
for relation_id in rerank_relation_ids:
for passage_id in relationid_2_passageids[relation_id]:
if passage_id not in final_passage_ids:
final_passage_ids.append(passage_id)
final_passages.append(passages[passage_id])
passages_from_our_method = final_passages[:final_top_k]
将结果与简单的 RAG 方法进行比较,后者基于查询嵌入直接从段落集合中检索 topK 个段落。简单的 RAG 检索到的段落遗漏了一个真实段落,这导致了错误的答案。图检索方法检索到的段落是正确的,这有助于得到问题的准确答案。
naive_passage_res = milvus_client.search(
collection_name=passage_col_name,
data=[query_embedding],
limit=final_top_k,
output_fields=["text"],
)[0]
passages_from_naive_rag = [res["entity"]["text"] for res in naive_passage_res]
print(
f"Passages retrieved from naive RAG: \n{passages_from_naive_rag}\n\n"
f"Passages retrieved from our method: \n{passages_from_our_method}\n\n"
)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"human",
"""Use the following pieces of retrieved context to answer the question. If there is not enough information in the retrieved context to answer the question, just say that you don't know.
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Answer:""",
)
]
)
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
answer_from_naive_rag = rag_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "context": "\n".join(passages_from_naive_rag)}
)
answer_from_our_method = rag_chain.invoke(
{"question": query, "context": "\n".join(passages_from_our_method)}
)
print(
f"Answer from naive RAG: {answer_from_naive_rag}\n\nAnswer from our method: {answer_from_our_method}"
)
Passages retrieved from naive RAG:
['Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.', 'Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782): The son of Johann Bernoulli, Daniel made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.']
Passages retrieved from our method:
['Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his relationship with the Bernoulli family was significant. Euler was born in Basel and was a student of Johann Bernoulli, who recognized his exceptional talent and mentored him in mathematics. Johann Bernoulli’s influence on Euler was profound, and Euler later expanded upon many of the ideas and methods he learned from the Bernoullis.', 'Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782): The son of Johann Bernoulli, Daniel made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics. He is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which describes the behavior of fluid flow and is fundamental to the understanding of aerodynamics.']
Answer from naive RAG: The son of Euler's teacher, Johann Bernoulli, was Daniel Bernoulli. Daniel made significant contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics, and is most famous for Bernoulli’s principle, which is fundamental to aerodynamics.
Answer: Daniel Bernoulli, the son of Euler's teacher, made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics, including the development of Bernoulli’s principle.
Answer from our method: The son of Euler's teacher, Johann Bernoulli, was Daniel Bernoulli. Daniel made significant contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics, and he is most famous for formulating Bernoulli’s principle, which is fundamental to aerodynamics and fluid flow.
Answer: Daniel Bernoulli, the son of Euler's teacher, made major contributions to fluid dynamics, probability, and statistics, and is best known for Bernoulli’s principle.